No products in the cart.
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark
🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇸🇰 Slovakia🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of America
and more
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark
🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇸🇰 Slovakia🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of America
and more
Acic cream 5% tube 2 g
$16.60
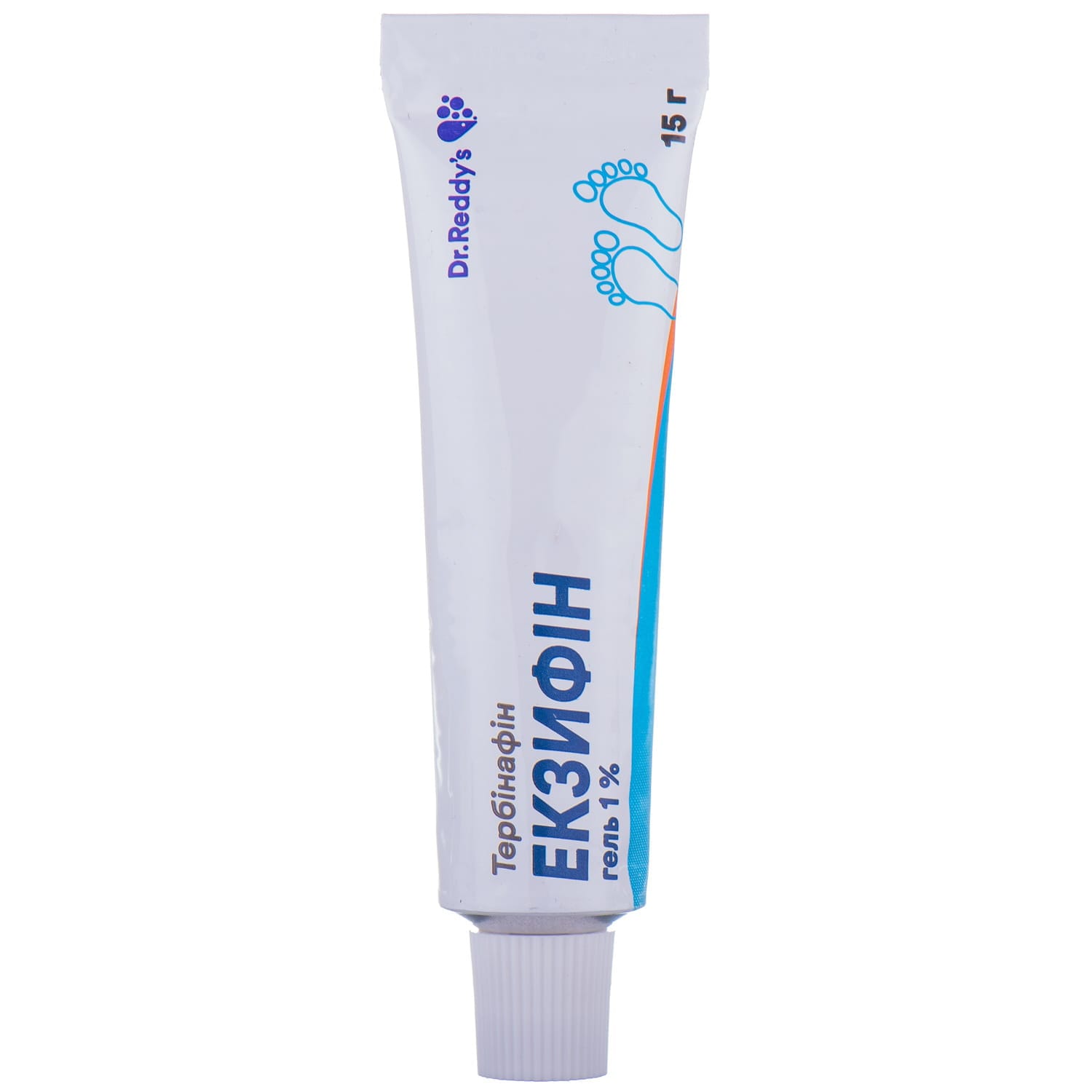
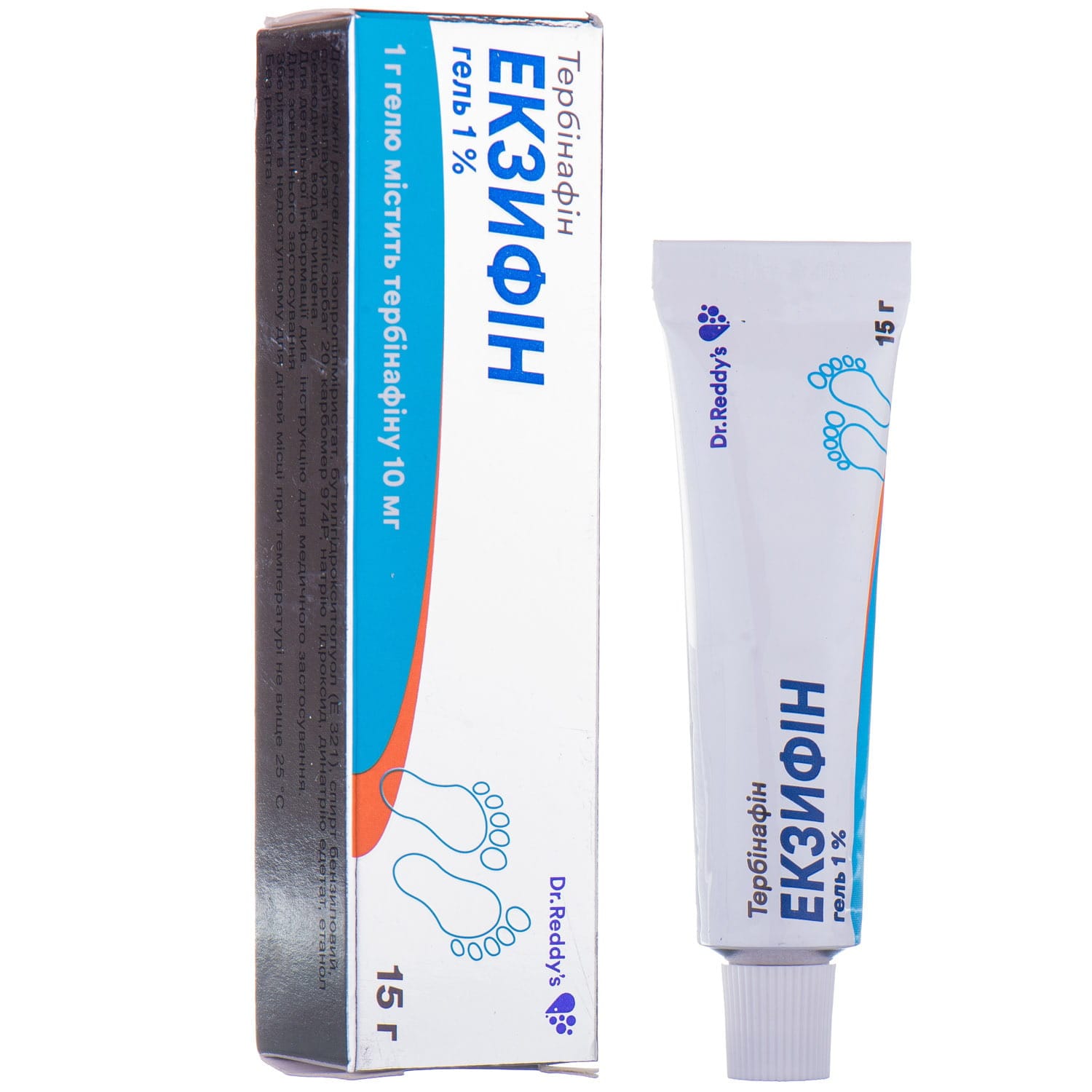
Exifine gel 1% tube 15 g
$16.21
Free Worldwide Shipping
to: Australia, Canada, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Poland, Slovakia, South Korea, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States and more
In stock
Exifine (terbinafine) treats skin and nail fungal infections. Oral and topical forms deliver potent antifungal action with deep tissue penetration.
Categories: Dermatology
Brand: Dr.Reddy's
Payment
PayPal, Debit or Credit card, Google Pay, Apple Pay
Pharmacological properties
A synthetic antifungal drug from the group of allylamines with a broad spectrum of antifungal activity. In low concentrations, it has fungicidal activity against dermatophytes, molds and some dimorphic fungi. The effect on yeast fungi can be fungicidal or fungistatic, depending on the type of fungi. The drug inhibits the biosynthesis of sterols in the fungal cell, which leads to ergosterol deficiency, the accumulation of squalene inside the cell and its death. Exifine does not affect the metabolism of hormones or other drugs. Exifine is effective against pathogens of dermatomycosis (Trichophyton spp., Microsporum canis and Epidermophyton floccosum), yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. Unlike topical application, its oral administration is ineffective in pytiriasis versicolor.
When administered orally, the drug accumulates in the skin and nails in fungicidal concentrations. 2 hours after taking 250 mg of terbinafine, its maximum concentration in the blood plasma is reached, which is 0.97 μg/ml; simultaneous food intake does not affect its bioavailability. Terbinafine is almost completely bound to blood plasma proteins (99%). It quickly diffuses through the dermis and accumulates in the lipophilic stratum corneum of the epidermis. It is secreted with the secretion of the sebaceous glands. High concentrations are created in hair follicles, hair, oily skin and in the nail plate. Biotransformation in the liver leads to the formation of metabolites that do not have antifungal activity and are excreted from the body mainly in the urine. The half-life is 17 hours. It does not accumulate in the body. No changes in pharmacokinetics have been observed depending on the patient’s age, however, in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function, the rate of drug excretion from the body may be reduced, resulting in higher terbinafine concentrations in the blood plasma.
Indication
Gel: fungal skin infections caused by dermatophytes such as Trichophyton (t. Rubrum, t. Mentagrophytes, t. Verrucosum, t. Violaceum), Microsporum canis and Epidermophyton floccosum, e.g. interdigital tinea pedis (“athlete’s foot”), inguinal tinea (“jock itch”), tinea corporis (“ringworm”). Tinea caused by Pityrosporum orbiculare (malassezia furfur).
Tablets: dermatomycoses (epidermophytosis of the skin and nail plates, rubromycosis, trichophytosis, microsporia), candidiasis of the skin and mucous membranes, mycotic lesions of the ENT organs, genitourinary system.
Application
Gel: apply to the skin once a day. Before applying the drug, it is necessary to thoroughly clean and dry the affected areas of the skin. The gel is applied in a thin layer to the affected skin and adjacent areas and rubbed in lightly. In case of diaper rash in skin folds (under the mammary glands, between the fingers, between the buttocks, in the groin area), the areas with the applied gel can be covered with gauze, especially at night.
Duration and frequency of gel application.
Dermatophytosis of the trunk, inguinal dermatophytosis: 1 time per day for 1 week.
Dermatophytosis of the feet (interdigital): 1 time per day for 1 week.
Usually, positive dynamics of the clinical picture of the disease are noted after a few days. Irregular use of the drug or premature discontinuation of treatment may lead to relapse.
No dose adjustment is necessary for elderly patients.
Due to lack of clinical experience, the drug should not be used in children.
Tablets: adults are prescribed Exifine orally at a dose of 250 mg once a day; children weighing 20 kg – 62.2 mg/day, 20-40 kg – 125 mg/day, 40 kg – 250 mg/day.
There are no data on the use of the drug in children under 2 years of age (body weight 12 kg).
The duration of treatment depends on the severity of the infection and the type of pathogen. Thus, for interdigital mycosis and lesions of the soles, the duration of treatment is 2-6 weeks, for tinea versicolor, cutaneous candidiasis – 24 weeks. Complete disappearance of the symptoms of the disease occurs after a few weeks. For onychomycosis, the duration of treatment in most cases is from 6 weeks to 3 months. With slow nail growth, a longer course of treatment may be required.
If there are no signs of improvement after 2 weeks, microbiological verification of the diagnosis is necessary.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to the drug, age up to 6 years, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Side effects
Possible feelings of fullness of the stomach, anorexia, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, skin rash. If allergic reactions occur, the drug is canceled.
Special instructions
Patients with severe renal and/or hepatic insufficiency should be prescribed the drug in lower doses. When prescribing the drug to elderly patients, the possibility of impaired liver or kidney function should be taken into account.
In experimental studies, no embryotoxic effects of terbinafine were detected, however, clinical experience of the drug in pregnant women is insufficient. It is not recommended to use the drug during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, in the absence of absolute indications for its use. Exifine passes into breast milk, so during treatment it is necessary to stop breastfeeding.
Interactions
It has a slight effect on the clearance of drugs that are metabolized with the participation of the cytochrome P450 system (cyclosporine, tolbutamide, oral contraceptives). Exifine elimination can be accelerated with simultaneous use of inducers of hepatic enzymes (rifampicin) and slowed down with simultaneous use of cytochrome P450 inhibitors (cimetidine). When used simultaneously with such drugs, Exifine dose adjustment is necessary.
Overdose
Cases of overdose have not been described. It can be assumed that acute overdose of the drug will be accompanied primarily by disorders of the digestive tract (nausea, vomiting). The stomach should be washed, activated charcoal should be prescribed, and symptomatic treatment should be carried out if necessary.
Storage conditions
In a dry, dark place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
You may also like