No products in the cart.
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark
🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇸🇰 Slovakia🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of America
and more
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark
🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇸🇰 Slovakia🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of America
and more
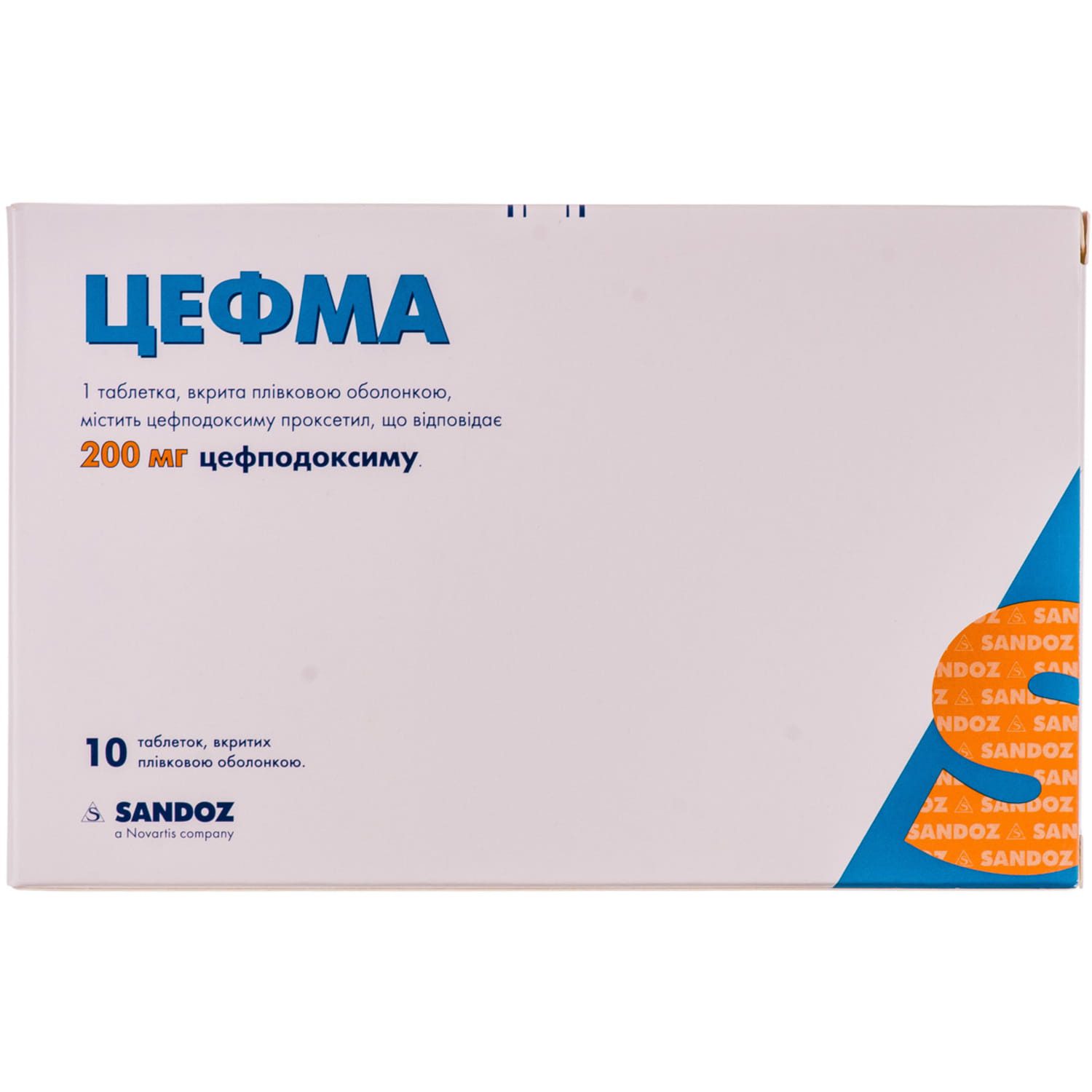
Cefma film-coated tablets 200 mg blister 10 pcs.
$37.59
Free Worldwide Shipping
to: Australia, Canada, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Poland, Slovakia, South Korea, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States and more
In stock
Cefma is an antibiotic belonging to the group of cephalosporins (a class of beta-lactam antibiotics). These drugs get their name from the beta-lactam ring in their chemical structure, which plays an important role in their mechanism of action. The main property of cephalosporins, including cefma, is that they disrupt the process of bacterial cell wall synthesis, which makes them effective against a wide range of microorganisms.
Categories: Cold and flu
Brand: Sandoz
Payment
PayPal, Debit or Credit card, Google Pay, Apple Pay
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Cefpodoxime exerts its antibacterial action by binding to and inhibiting the action of certain bacterial cell wall synthetic enzymes, namely penicillin-binding proteins. This leads to interruption of cell wall (peptidoglycan) biosynthesis, which leads to lysis and death of bacterial cells.
In vitro, cefpodoxime has bactericidal activity against numerous gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.
Cefpodoxime has high activity against gram-positive microorganisms: Streptococcus pneumoniae; Streptococci groups A (S. pyogenes), B (S. agalactiae), C, F and G; other Streptococci (S. mitis, S. sanguis and S. salivarius); Corynebacterium diphtheriae.
Cefpodoxime has high activity against gram-negative microorganisms: Haemophilus influenza (strains that produce and do not produce β-lactamase), Haemophilus parainfluenza (strains that produce and do not produce β-lactamase), Branhamella catarrhalis (strains that produce and do not produce β-lactamase), Neisseria meningitidis; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; Escherichia coli; Klebsiella spp. (K. pneumoniae, K. oxytoca), Proteus mirabilis.
Moderately sensitive to cefpodoxime are: methicillin Staphylococci, strains that produce and do not produce penicillinase (S. aureus and S. epidermidis).
Cefpodoxime-resistant: Enterococci; methicillin-resistant Staphylococci (S. aureus and S. epidermidis), Staphylococcus saprophyticus; Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas spp.; Clostridium difficile; Bacteroides fragilis and related species.
If possible, susceptibility should be determined by in vitro testing.
Pharmacokinetics
Cefpodoxime proxetil is absorbed in the intestine and hydrolyzed to the active metabolite cefpodoxime. When cefpodoxime proxetil is administered orally to fasting subjects in tablet form, equivalent to 100 mg of cefpodoxime, 51.1% is absorbed, and absorption increases with food. The volume of distribution is 32.3 L, and peak levels of cefpodoxime are reached 2-3 hours after administration. C max in plasma is 1.2 and 2.5 mg/L after doses of 100 and 200 mg, respectively. After administration of 100 and 200 mg 2 times a day for 14.5 days, the pharmacokinetics of cefpodoxime in plasma remains unchanged. The binding of cefpodoxime to plasma proteins is 40%, mainly to albumin. This is an unsaturated bond. Concentrations of cefpodoxime exceeding the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) for common pathogens can be achieved in lung parenchyma, bronchial mucosa, pleural fluid, tonsils, interstitial fluid, and prostate tissue. Studies in healthy volunteers show that mean concentrations of cefpodoxime in total ejaculate 6-12 hours after a single 200 mg dose are above the MIC90 for N. gonorrhoeae. Since most of the cefpodoxime is excreted in the urine, the concentration is high. (MICs at time intervals 0-4, 4-8, 8-12 hours after a single dose exceed the MIC90 for common urinary pathogens). Good diffusion of cefpodoxime is also observed in renal tissue, with concentrations above MIC 90 for common urinary pathogens occurring 3-12 hours after a single dose of 200 mg (1.6-3.1 μg/g). Cefpodoxime concentrations in brain and cerebral cortex tissues are similar. The main route of excretion is renal, with 80% excreted unchanged in the urine with a T½ of about 2.4 hours.
Indication
Treatment of infections caused by pathogens sensitive to the drug:
- ENT infections (including sinusitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis); for the treatment of tonsillitis and pharyngitis, cefpodoxime is prescribed for chronic or recurrent infection, as well as in cases of known or suspected insensitivity of the pathogen to widely used antibiotics;
- respiratory tract infections (including acute bronchitis, relapses or exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, bacterial pneumonia);
- uncomplicated upper and lower urinary tract infections (including acute pyelonephritis and cystitis);
- skin and soft tissue infections (abscess, cellulitis, infected wounds, furuncle, folliculitis, paronychia, carbuncle and ulcer);
- uncomplicated gonococcal urethritis.
Application
The drug is administered orally. For optimal absorption, the tablet should be taken with food.
Adults and adolescents with normal renal function
Sinusitis: 200 mg 2 times a day.
Tonsillitis and pharyngitis: 100 mg 2 times a day.
Acute bronchitis, exacerbation of chronic bronchitis and bacterial pneumonia: 100-200 mg 2 times a day, depending on the severity of the disease.
Uncomplicated urinary tract infections: 100 mg 2 times a day.
Uncomplicated upper urinary tract infections: 200 mg 2 times a day.
Skin and soft tissue infections: 200 mg 2 times a day.
Uncomplicated gonococcal urethritis: 200 mg as a single dose.
Elderly patients: No dose adjustment is necessary in elderly patients with normal renal function.
Hepatic impairment: No dose adjustment is required for patients with hepatic impairment.
Renal impairment: Appropriate dose adjustment is required for patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance 40 ml/min).
| Creatinine clearance, ml/min | dosage |
|---|---|
| 39-10 | A single dose of 1 is administered every 24 hours (i.e. ½ adult dose) |
| 10 | A single dose of 1 is administered every 48 hours (i.e. ¼ dose for adults) |
| hemodialysis | A single dose of 1 is administered after each dialysis session. |
1 Single dose of 100 or 200 mg depending on the type of infection as indicated above.
The duration of therapy depends on the patient, indications, and pathogen.
Contraindication
Hypersensitivity to cefpodoxime, cephalosporin drugs or any component of the drug. History of immediate or severe hypersensitivity reactions to penicillin or any other beta-lactam drug. Rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome.
Side effects
To determine the frequency of adverse reactions, the following classification was used: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100, 1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000, 1/100), rare (≥1/10,000, 1/1000), very rare (1/10,000, including isolated cases).
From the digestive system: often – anorexia, intragastric pressure, gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, flatulence, diarrhea. Bloody diarrhea may be a symptom of enterocolitis; rarely – thirst, tenesmus, dyspepsia, dry mouth, decreased appetite, constipation, candidal stomatitis, belching, gastritis, mouth ulcers, acute pancreatitis, pseudomembranous colitis.
Metabolic: often – loss of appetite; rarely – dehydration, gout, peripheral edema, weight gain.
Immune system disorders: uncommon – hypersensitivity; rare – anaphylactic reactions, bronchospasm and angioedema; life-threatening shock.
From the hepatobiliary system: infrequently – cholestatic liver damage.
Laboratory indicators: infrequently – transient increase in the activity of liver transaminases AST, ALT, GLP and / or bilirubin, urea and creatinine, pseudo-positive Coombs’ test; rarely – acute hepatitis.
From the blood system: rarely – hematological disorders
Be the first to review “Cefma film-coated tablets 200 mg blister 10 pcs.” Cancel reply
You may also like









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.