No products in the cart.
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark
🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇸🇰 Slovakia🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of America
and more
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark
🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇸🇰 Slovakia🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of America
and more

Le’Saffron tablets for r...
$25.94
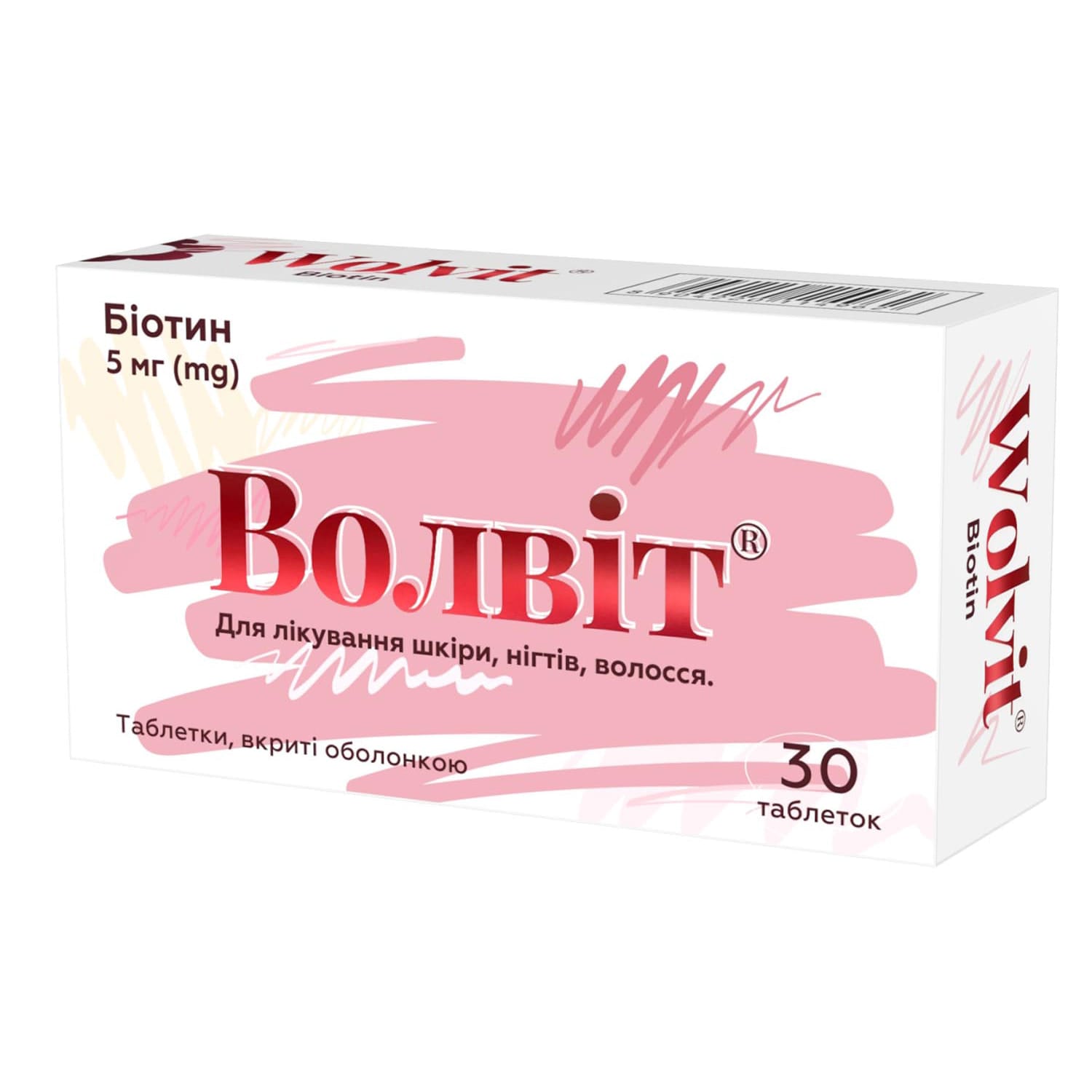
Wolvit film-coated tablets 5 mg, 30 pcs
$23.16
Free Worldwide Shipping
to: Australia, Canada, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Poland, Slovakia, South Korea, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States and more
In stock
Wolvit tablets 5 mg support hair, skin, and nail health, treating biotin deficiency and related enzymatic disorders safely.
Categories: Vitamins and supplements
Brand: Kusum Healthcare
Payment
PayPal, Debit or Credit card, Google Pay, Apple Pay
Pharmacological Properties
Pharmacodynamics
Biotin (vitamin H, vitamin B7) is a water-soluble B-group vitamin. In the body, biotin plays an essential role in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, and is vital for normal cell growth and development. After entering the body, biotin acts as a coenzyme of carboxylases, exhibits insulin-like activity, and participates in gluconeogenesis (due to involvement in glucokinase synthesis), thereby helping stabilize blood glucose levels and improving nervous system function. Biotin is a synergist of other B vitamins, folic acid, pantothenic acid, and cyanocobalamin. There is evidence of biotin participation in the synthesis of purine nucleotides. Biotin is also a source of sulfur involved in protein synthesis—specifically collagen—which positively affects the structure of the skin and its appendages (hair and nails).
Biotin deficiency may occur due to unbalanced nutrition, prolonged diets, consumption of raw egg whites; during parenteral nutrition; in malabsorption syndrome; after resection of the small intestine; in biotin-related multiple carboxylase deficiency; and in patients undergoing hemodialysis.
Pharmacokinetics
Biotin is rapidly absorbed in the small intestine via passive diffusion, then enters the liver through the portal system and subsequently reaches systemic circulation. Protein binding is approximately 80%. The concentration of free or weakly bound biotin in blood is typically 200–1200 mcg/L. Biotin crosses the blood–brain and placental barriers. It is metabolized into various metabolites and excreted unchanged via urine (6–50 mcg/day) and feces (approximately 50%), as well as in the form of biologically inactive metabolites. The half-life depends on the administered dose and is about 26 hours after oral intake of 100 mcg/kg body weight. In patients with biotinidase deficiency, the half-life decreases to 10–14 hours.
Indications
Treatment of conditions caused by biotin deficiency: diseases of the skin, nails, and hair.
Treatment of genetically determined enzymopathies associated with biotin (multiple carboxylase deficiency).
Administration
Wolvit tablets should be taken orally by adults. Take before meals with a small amount of water.
Nail, hair, and skin disorders: recommended dose is 5 mg (1 tablet) daily.
Genetically determined enzymopathies (multiple carboxylase deficiency): 2–4 tablets (up to 20 mg biotin daily) in 1–2 doses.
Duration of treatment depends on the condition and course of the disease; typically 1 month.
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to biotin or other components of the product.
Side Effects
Immune system: allergic reactions, including chest pain, shortness of breath, urticaria, and skin rash.
Special Warnings
Do not interrupt the treatment duration prescribed by the physician. Interrupting or stopping therapy prematurely may reduce effectiveness. Due to good tolerability, long-term treatment is possible.
The product contains Ponceau 4R (E124), which may cause allergic reactions.
Pregnancy and Lactation
No data on the use of this medicinal product during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Ability to Drive and Use Machinery
No data on negative effects on reaction speed.
Children
The product is not intended for use in children.
Interactions
Concurrent use with antiepileptic drugs may reduce biotin plasma levels due to increased excretion. Valproic acid reduces biotinidase activity, affecting mitochondrial function in the liver.
Raw egg white contains the protein avidin, which interacts with biotin; therefore, simultaneous consumption should be avoided. Consuming large quantities of raw eggs for 2–3 weeks may cause biotin deficiency.
High doses of pantothenic acid compete with biotin; avoid simultaneous administration.
Overdose
No reports of biotin overdose.
Storage Conditions
Store at temperatures not exceeding 25°C.
Be the first to review “Wolvit film-coated tablets 5 mg, 30 pcs” Cancel reply
You may also like







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.