No products in the cart.
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more

Ascoril tablets 20 pieces
$22.69
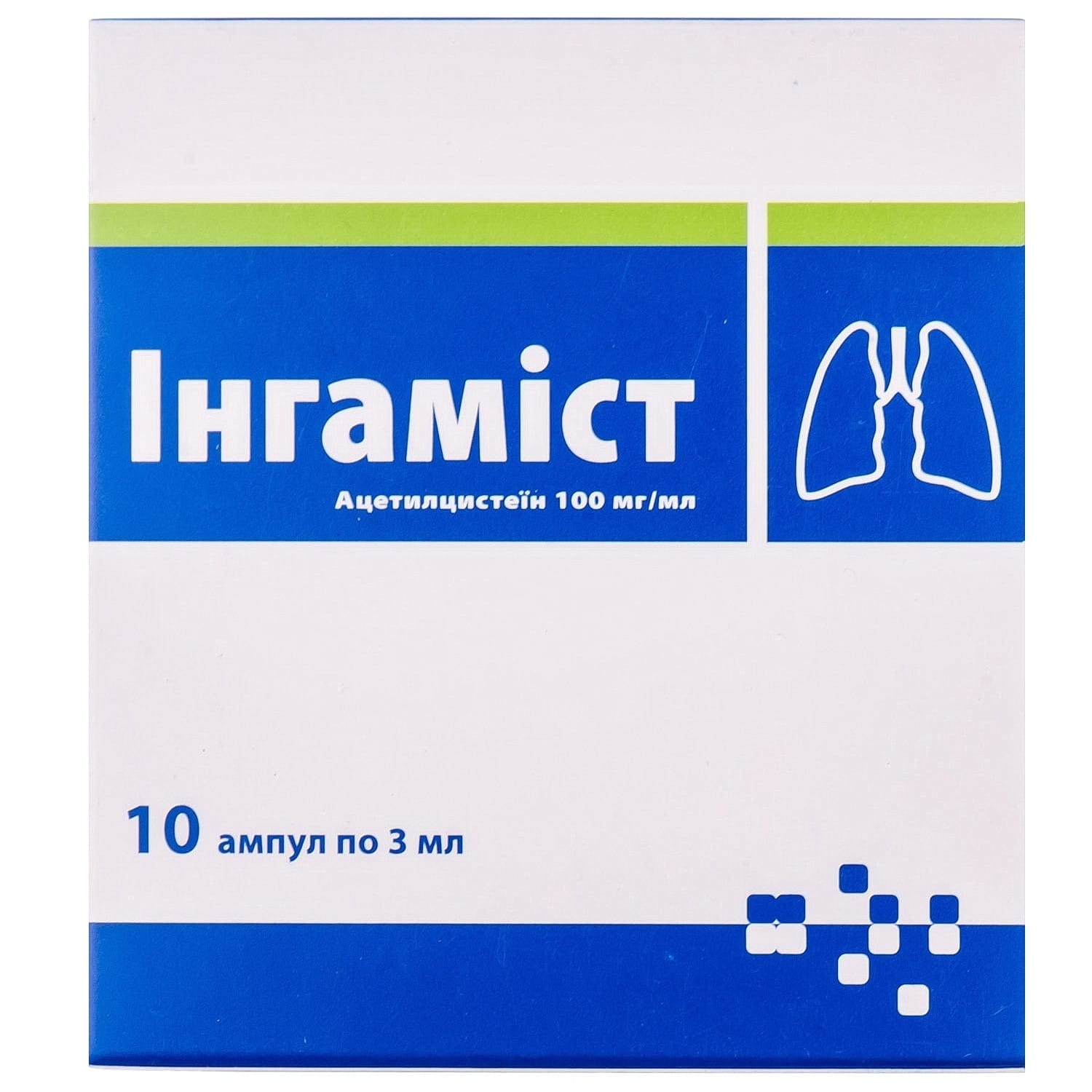
Ingamist solution for injection 100 mg/ml in 3 ml ampoules 10 pcs.
$42.61
Free Worldwide Shipping
to: Australia, Canada, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Poland, South Korea, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States and more
In stock
INGAMIST 100 mg/ml acetylcysteine injection for respiratory diseases. Provides mucolytic action, dosing details, key indications, and important safety info.
Categories: Cold and flu
Brand: Yuria-Pharm
Payment
PayPal, Debit or Credit card, Google Pay, Apple Pay
INGAMIST solution for injection 100 mg/ml
Composition:
Active ingredient: acetylcysteine;
1 ml contains acetylcysteine 100 mg
Excipients: sodium edetate, sodium hydroxide, water for injections.
Dosage form.
Solution for injection
Main physicochemical properties: clear colorless liquid with a faint sulfur odor.
After opening the ampoule, a faint pink-purple hue may appear upon prolonged contact with air.
Pharmacotherapeutic group.
Mucolytic agent. ATS code r05c B01.
Pharmacological properties.
Pharmacodynamics.
Acetylcysteine thins sputum. In the structure of acetylcysteine, sulfhydryl groups contribute to the rupture of disulfide bonds of acidic mucopolysaccharides of sputum, which leads to depolarization of mucoproteins and a decrease in mucus viscosity. The drug retains activity in the presence of purulent sputum.
Acetylcysteine has an antioxidant effect due to the presence of a nucleophilic thiol SH-group, easily donates hydrogen, neutralizing oxidative radicals.
The protective mechanism of acetylcysteine is based on the ability of its reactive sulfhydryl groups to bind free radicals.
Acetylcysteine easily penetrates the cell, is deacetylated to L-cysteine, from which intracellular glutathione is synthesized.
Glutathione is a highly reactive tripeptide, a powerful antioxidant, cytoprotector, capturing endogenous and exogenous free radicals, toxins. Acetylcysteine prevents depletion and helps increase the synthesis of intracellular glutathione, which participates in redox processes of cells, thus contributing to the detoxification of harmful substances.
Pharmacokinetics.
With intravenous administration of 600 mg of acetylcysteine, the maximum concentration in the blood plasma is 300 mmol / l, the half-life of the blood is 2 hours. Total clearance is 0.21 l / h / kg, and the volume of distribution at the plateau is 0.34 l / kg. Acetylcysteine \u200b\u200bis penetrates into the intercellular space, is mainly distributed in the liver, kidneys, lungs, bronchial secretions. Acetylcysteine \u200b\u200band its metabolites are excreted mainly by the kidneys.
Clinical characteristics.
Indication.
Acute and chronic respiratory diseases accompanied by increased sputum production.
Contraindication.
Hypersensitivity to acetylcysteine or to other components of the drug, gastric and duodenal ulcer in the acute stage, hemoptysis, pulmonary hemorrhage.
Interaction with other drugs and other types of interactions.
Concomitant use of acetylcysteine with antitussives may increase sputum congestion due to suppression of the cough reflex.
Concomitant administration of acetylcysteine and nitroglycerin may lead to increased vasodilator effects of the latter. Patients should be warned about the possibility of a decrease in blood pressure and headache.
It is not recommended to use antibiotics and acetylcysteine in the same syringe: a decrease in the activity of antibiotics is possible.
Due to its ability to form chelate structures, acetylcysteine can reduce the bioavailability of salts of metals such as gold, calcium, and iron. Therefore, it is recommended to use these drugs at different times.
laboratory indicators
The use of acetylcysteine may alter the results of colorimetric salicylate quantification, as well as the results of urine ketone determination.
Application features.
Patients with bronchial asthma should be under the supervision of a physician during therapy with Ingamist. In case of bronchospasm, acetylcysteine should be discontinued immediately.
Ingamist should be used with caution in patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease, especially in case of concomitant administration of other drugs that irritate the gastric mucosa.
Taking acetylcysteine, especially at the beginning of therapy, makes the secretion of the bronchial glands less viscous and may increase its volume. If the patient cannot cough up sputum effectively, postural drainage and aspiration of bronchial contents should be performed.
Intravenously, the drug should be administered under strict medical supervision. Side effects from intravenous administration of acetylcysteine may occur more often if the drug is administered too quickly or in large doses. Therefore, it is recommended to strictly follow the instructions given in the sections “Method of administration and dosage”.
This medicinal product contains 43 mg (1.9 mmol) of sodium per ampoule. This should be taken into consideration by patients on a controlled sodium diet.
Ingamist solution should not come into contact with rubber and metal surfaces.
The faint sulfuric odor of the solution is the characteristic odor of the active substance.
For intravenous administration, open the ampoule immediately before using the drug. For topical use, partial use of the ampoule contents is possible: the remaining solution can be used (subject to storage conditions) within 24 hours for topical use only; the remaining solution for injection is prohibited.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, the use of acetylcysteine is possible only if the intended benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus or child, under the direct supervision of a physician.
The ability to influence the reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms.
There is no data to support an effect on reaction rate.
Method of administration and doses.
topical application
Inhalation: adults 1 ampoule 1-2 times a day as prescribed by a doctor for 5-10 days, children from 6 years old – up to 1 ampoule 1-2 times a day as prescribed by a doctor for 5-10 days.
Endobronchial administration: adults and children from 6 years old – up to 1 ampoule 1-2 times a day.
Systemic application
intramuscular injection
Adults – 1 ampoule of 300 mg 1-2 times a day, administered deeply intramuscularly.
intravenous injection
The drug should be administered slowly drip in 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution.
Adults: 1 ampoule of 300 mg 1-2 times a day.
Children.
The drug is not used for intramuscular and intravenous administration to children (preferably oral dosage forms).
For topical use, the drug should be prescribed to children over 6 years of age.
Overdose.
When administered intravenously
symptoms
Symptoms of overdose are similar to symptoms of severe adverse reactions.
treatment
Treatment requires immediate discontinuation of the drug and symptomatic therapy. There is no specific antidote. Dialysis is effective.
When applied topically
symptoms
High doses may cause the production of large amounts of bronchopulmonary secretions, which may lead to airway obstruction.
treatment
Mechanical removal of mucus from the tracheobronchial tree.
Adverse reactions.
With local application, the following reactions are possible:
On the part of the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions;
Respiratory system: bronchospasm, rhinorrhea;
On the part of the digestive system: stomatitis, nausea, vomiting;
Skin: urticaria, rash, itching.
With parenteral use, the following reactions are possible:
Immune system disorders: anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic reaction, anaphylactoid reactions, hypersensitivity;
From the cardiovascular system: tachycardia, decreased blood pressure;
Respiratory: bronchospasm, dyspnea
On the part of the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia, heartburn;
On the part of the skin: angioedema, urticaria, hyperemia,
burning sensation at the injection site, rash, itching, in rare cases the development of the syndrome is possible
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Lyell’s syndrome;
Others: facial edema, headache, tinnitus, hemorrhages, hyperthermia, anemia, increased prothrombin time.
Expiration date.
2 years.
Storage conditions.
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C in the original packaging.
Keep out of reach of children.
Incompatibility.
The ingamist solution should not come into contact with rubber and metal surfaces.
Packaging.
3 ml in dark glass ampoules; 5 ampoules in a contour blister pack; 2 contour packs in a pack.
Be the first to review “Ingamist solution for injection 100 mg/ml in 3 ml ampoules 10 pcs.” Cancel reply
You may also like







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.