🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more
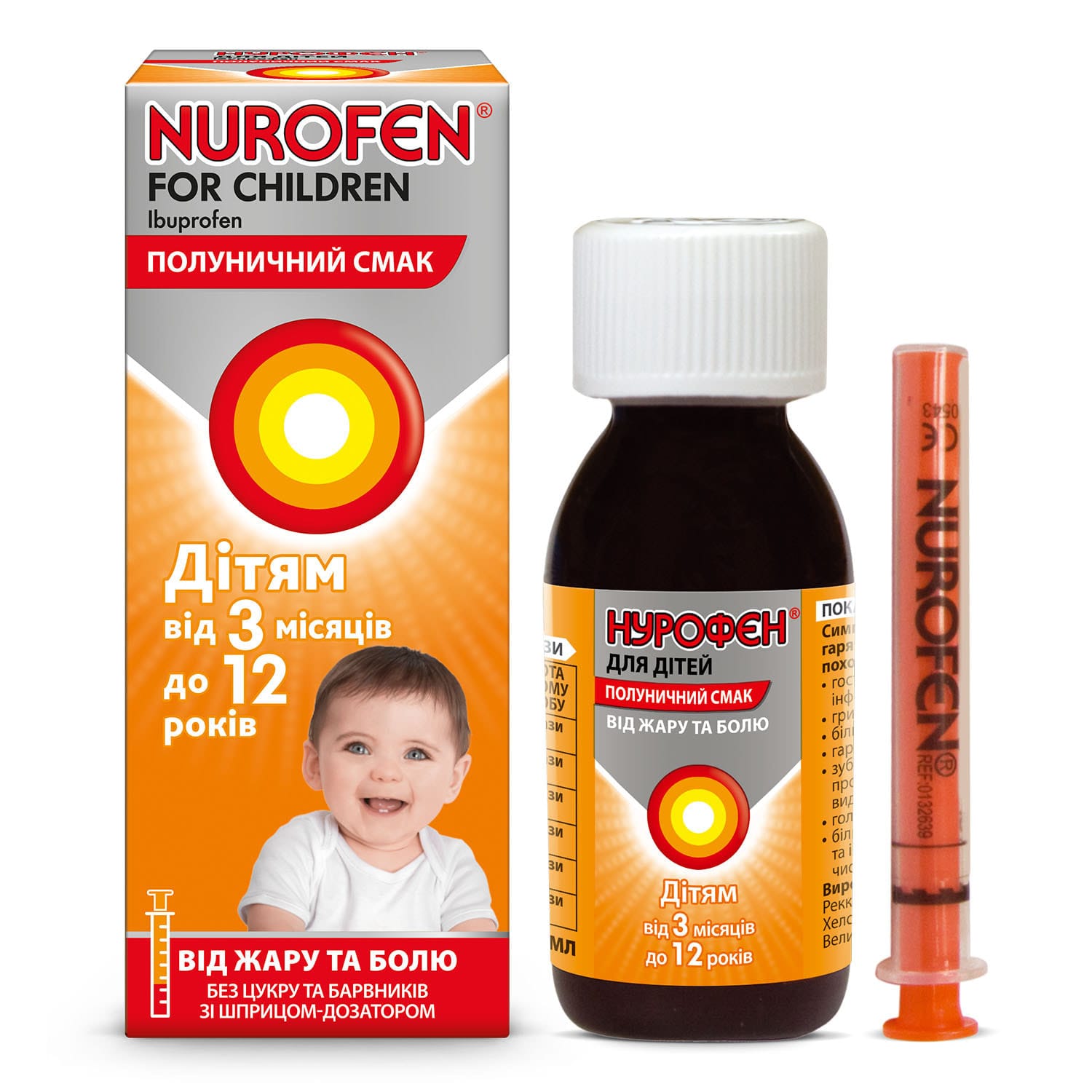
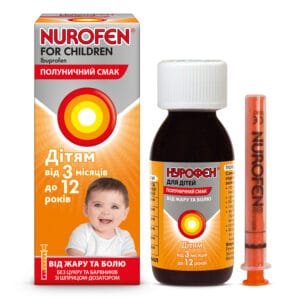
Nurofen for children oral suspension with strawberry flavor 100 mg/5 ml bottle 100 ml with dosing syringe
$19.91
Nurofen for Children Strawberry treats fever and pain in kids aged 3 months to 12 years. Effective relief for teething, colds, flu and inflammation.
-
— or —
Oral suspension with strawberry flavor “Nurofen for children” is used for the symptomatic treatment of fever and pain of various origins in children aged 3 months to 12 years with a body weight of at least 5 kg (including fever after immunization, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, teething pain, pain after tooth extraction, toothache, headache, sore throat, pain from sprained ligaments and other types of pain, including inflammatory genesis).
Composition
The active substance is ibuprofen (5 ml of suspension contains 100 mg of ibuprofen).
Excipients: liquid maltitol; citric acid, monohydrate; sodium citrate; sodium chloride, sodium saccharin, domiphene bromide; polysorbate 80; xanthan gum; strawberry flavoring 5002442; glycerin; purified water.
Contraindication
- hypersensitivity to ibuprofen or to any of the excipients of the drug;
- history of hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. bronchospasm, bronchial asthma, rhinitis, angioedema or urticaria) after taking acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- gastric ulcer/bleeding in active form or history of recurrence (two or more severe episodes of confirmed ulcer or bleeding);
- history of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation associated with NSAID use;
- severe liver failure, severe kidney failure, or severe heart failure;
- severe dehydration (caused by vomiting, diarrhea, or insufficient fluid intake);
- the last trimester of pregnancy;
- cerebrovascular or other bleeding;
- disorders of hematopoiesis of unknown etiology or blood clotting;
- hereditary fructose intolerance.
Method of application
Side effects can be minimized by using the lowest effective dose necessary to control symptoms for the shortest period of time.
For oral use. The recommended daily dose is 20-30 mg per kg of body weight, divided into equal doses depending on age and body weight, with an interval between doses of 6-8 hours. To ensure accurate dosing, the package contains a dosing syringe. The recommended dose should not be exceeded. For short-term use only.
Recommended dosage:
- at the age of 3-6 months (5-7.6 kg) – 2.5 ml of suspension (50 mg) no more than 3 times a day;
- at the age of 6-12 months (7.7-9 kg) – 2.5 ml of suspension (50 mg) no more than 3-4 times a day;
- at the age of 1-3 years (10-16 kg) – 5 ml of suspension (100 mg) no more than 3 times a day;
- at the age of 4-6 years (17-20 kg) – 7.5 ml of suspension (150 mg) no more than 3 times a day;
- at the age of 7-9 years (21-30 kg) – 10 ml of suspension (200 mg) no more than 3 times a day;
- at the age of 10-12 years (31-40 kg) – 15 ml of suspension (300 mg) no more than 3 times a day.
Do not use on children under 3 months of age unless recommended by a doctor.
Do not use the drug for children weighing less than 5 kg.
For children 3 to 6 months of age, if symptoms persist for more than 24 hours after the start of treatment or worsen (after 3 doses), you should consult a doctor immediately.
If symptoms persist for more than 3 days after the start of treatment or worsen in children aged 6 months to 12 years, you should consult a doctor.
For fever after immunization (children aged 3-6 months), the recommended daily dose is 2.5 ml of suspension (50 mg), if necessary – another 2.5 ml of suspension (50 mg) after 6 hours, but not more than 5 ml of suspension (100 mg) within 24 hours. If symptoms persist, you should consult a doctor.
Patients with sensitive stomachs should take the drug with meals.
Shake before use.
Application features of Nurofen for children
Pregnant women
The drug is used in children under 12 years of age. Ibuprofen should not be taken during the first two trimesters of pregnancy unless, in the opinion of the doctor, the potential benefit to the patient outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. If ibuprofen is used by a woman trying to conceive, or during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, the lowest possible dose should be used for the shortest possible period of time. Ibuprofen is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Ibuprofen and its metabolites are excreted in breast milk in low concentrations. There are currently no known adverse effects on the infant, so for short-term treatment of pain and fever at recommended doses, it is usually not necessary to interrupt breastfeeding.
There is some evidence that drugs that inhibit cyclooxygenase/prostaglandin synthesis may impair female fertility by affecting ovulation. This effect is reversible upon discontinuation of treatment. Therefore, the use of ibuprofen is not recommended in women who have difficulty conceiving.
Drivers
The drug is used in children under 12 years of age. When used according to the recommended doses and duration of treatment, the drug is not expected to affect the ability to drive or operate other mechanisms.
Overdose
In children, symptoms of overdose may occur when taking ibuprofen doses exceeding 400 mg/kg. In adults, dose reactions are less pronounced. The half-life in overdose is 1.5-3 hours.
Symptoms
In most patients, the use of clinically significant amounts of NSAIDs caused only nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain or, less commonly, diarrhea. Tinnitus, headache and gastrointestinal bleeding may also occur. In more severe poisoning, toxic lesions of the central nervous system are possible in the form of vertigo, dizziness, drowsiness, sometimes – an excited state and disorientation or coma. Sometimes patients develop convulsions. In severe poisoning, hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis may occur, as well as an increase in PV / INR (probably due to interaction with blood clotting factors circulating in the bloodstream). Acute renal failure, liver damage, hypotension, respiratory depression and cyanosis may occur. In patients with bronchial asthma, exacerbation of asthma is possible. Nystagmus, impaired visual acuity and loss of consciousness are possible.
Treatment
There is no specific antidote. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive, and include maintaining a patent airway and monitoring cardiac function and vital signs until the patient is stable. Consider oral administration of activated charcoal or gastric lavage if the patient has taken a potentially toxic dose within one hour. If ibuprofen has already been absorbed, alkaline agents may be used to help eliminate acidic ibuprofen in the urine. Intravenous diazepam or lorazepam may be used for frequent or prolonged seizures. Bronchodilators should be used for exacerbations of asthma. Medical advice should be sought.
Side effects of Nurofen for children
The most frequently observed adverse reactions are from the gastrointestinal tract. In general, adverse reactions are dose-dependent. In particular, the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding depends on the dose and duration of treatment. Gastrointestinal ulcers, perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding, sometimes fatal, may occur, especially in elderly patients. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal distension, constipation, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, melena, haematemesis, ulcerative stomatitis, exacerbation of colitis and Crohn’s disease have been reported after the use of ibuprofen. Gastritis has been observed less frequently.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C, out of the reach of children.
Shelf life – 3 years.
You may also like















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.