No products in the cart.
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more

Artiflex cream tube 100 g
$24.96
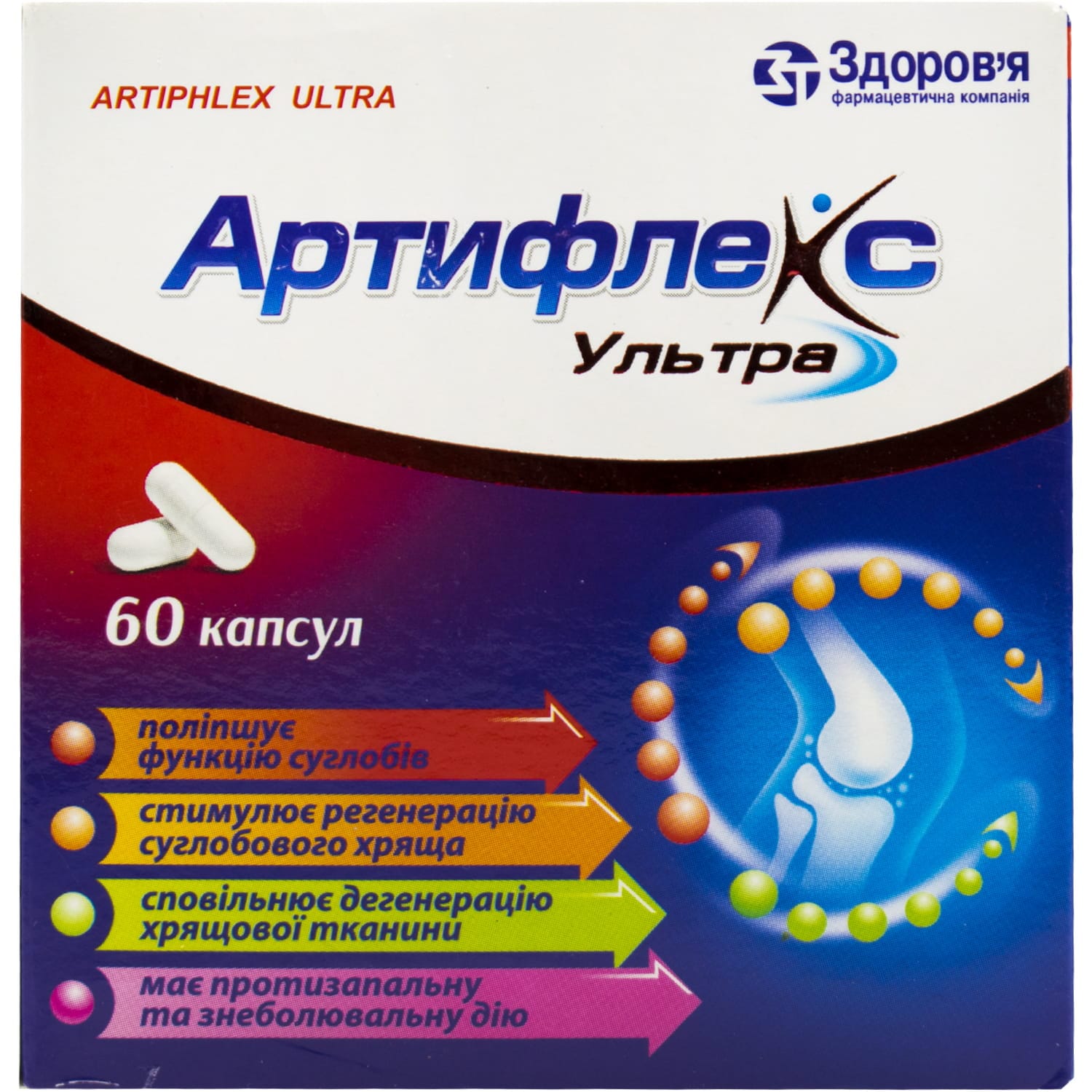
Artiflex Ultra capsules 60 pcs.
$28.73
Free Worldwide Shipping
to: Australia, Canada, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Poland, South Korea, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States and more
In stock
Artiflex Ultra relieves joint pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis. With glucosamine, chondroitin and ibuprofen to support cartilage health.
Category: Gastrointestinal tract and liver
Brand: Zdorovye
Payment
PayPal, Debit or Credit card, Google Pay, Apple Pay
Composition of the medicinal product:
active substances: 1 capsule contains glucosamine sulfate sodium chloride in terms of glucosamine sulfate 250 mg, chondroitin sodium sulfate 200 mg, ibuprofen 100 mg;
excipients: pregelatinized starch, crospovidone, sodium starch glycolate (type A), stearic acid, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, povidone, colloidal anhydrous silicon dioxide; capsule shell contains: gelatin, titanium dioxide (E 171).
Dosage form: Capsules.
Hard gelatin capsules of white color. The contents of the capsules are a mixture containing granules and powder from white to almost white color. The presence of agglomerates of particles is allowed.
The enterprise trademark – ZT is allowed to be applied to the capsule.
Name and location of the manufacturer.
LLC “Pharmaceutical company” Zdorovya “.
Ukraine, 61013, Kharkov, ul. Shevchenko, 22.
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
Combined anti-inflammatory (antirheumatic) agents.
ATC code: M01B.
Chondroitin sulfate sodium is a high-molecular polysaccharide that participates in the construction of cartilage tissue, reduces the activity of enzymes that destroy articular cartilage, and stimulates the regeneration of articular cartilage. In the early stages of the inflammatory process, chondroitin sulfate sodium inhibits its activity and, thus, slows down the degeneration of cartilage tissue. Helps reduce pain, improves joint function and reduces the need for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joints.
Glucosamine sulfate has chondroprotective properties, reduces the deficiency of glycosaminoglycans in the body and participates in the synthesis of proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid.
Due to its ability to selectively affect cartilage tissue, glucosamine initiates the process of sulfur fixation during the synthesis of chondroitin sulfate. Glucosamine sulfate selectively affects articular cartilage, is a specific substrate and stimulator of the synthesis of hyaluronic acid and proteoglycans, inhibits the formation of superoxide radicals and enzymes that cause damage to cartilage tissue (collagenase and phospholipase), prevents the destructive effect of glucocorticoids on chondrocytes and disruption of the biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Ibuprofen has antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. The mechanism of action is associated with non-selective blocking of cyclooxygenase (COX) types 1 and 2 (the main enzyme in the metabolism of arachidonic acid), which leads to a decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins, a decrease in their concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid and a decrease in the excitation of the thermoregulation center. Reduces morning stiffness, helps to increase the volume of movements in the joints and spine.
After oral administration of a single therapeutic dose, the maximum level of sodium chondroitin sulfate in the blood plasma is reached after 3-4 hours, in the synovial fluid – after 4-5 hours. Bioavailability is 13%. It is excreted within 24 hours, mainly by the kidneys.
After oral administration, 90% of glucosamine is absorbed in the intestines. More than 25% of the applied dose enters the cartilage tissue and synovial membranes of the joints from the blood plasma. In the liver, part of the drug is metabolized to urea, carbon dioxide and water. The bioavailability of glucosamine is 25% due to the first passage through the liver. The highest concentrations of glucosamine are determined in the liver, kidneys and articular cartilage. About 30% of the dose taken persists for a long time in bone and muscle tissues. It is excreted mainly unchanged in the urine, partly in the feces. The half-life is 68 hours.
After oral administration, ibuprofen is almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Simultaneous food intake delays absorption. Ibuprofen is metabolized in the liver (90%). The half-life is 2-3 hours. 80% of the dose is excreted in the urine, mainly in the form of metabolites.
Indications for use:
Treatment of pain syndrome in primary and secondary osteoarthritis of the joints of the extremities and intervertebral discs.
Contraindications:
This medicine is contraindicated in the following cases:
- increased individual sensitivity to the active substances or to other ingredients of the drug;
- the patient has a history of bronchospasm, asthma, rhinitis, or skin rashes associated with the use of acetylsalicylic acid or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- the patient has a history of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation after taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs);
- gastric ulcer/bleeding now or in history (two or more pronounced episodes of exacerbation of ulcer and bleeding);
- optic nerve disease;
- hematopoiesis disorders;
- severe renal, cardiac or hepatic failure;
- phenylketonuria;
- pregnancy or breastfeeding.
The use of the drug simultaneously with other NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors, is contraindicated.
Appropriate precautions for use.
The use of Artiflex Ultra should be avoided simultaneously with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If acetylsalicylic acid is used to inhibit platelet aggregation, a doctor should be consulted before starting treatment with the drug.
For patients with liver or kidney disease, additional examinations are recommended before starting treatment: monitoring of liver and kidney function and peripheral blood tests.
Elderly people with a history of gastrointestinal diseases are at increased risk of adverse reactions when using NSAIDs, especially in the form of gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be used with caution in patients with a history of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, as their condition may worsen.
There is evidence that drugs that slow down cyclooxygenase / prostaglandin synthesis can cause impaired fertility in women due to their effect on ovulation. This can be avoided by stopping the use of these drugs.
It is not recommended to drink alcohol during treatment with Artiflex Ultra.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with:
- systemic lupus erythematosus and systemic connective tissue diseases – increased risk of aseptic meningitis;
- a history of arterial hypertension and/or heart failure, which were accompanied by fluid retention and edema during the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- impaired kidney and/or liver function.
Special precautions.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
There are no clinical data on the safety and efficacy of Artiflex Ultra during pregnancy or breastfeeding, so the drug should not be prescribed during these periods.
The ability to influence the reaction rate when driving vehicles or working with other mechanisms is unknown.
Children: There is no experience with the use of the drug in children under 12 years of age.
Method of administration and doses.
The drug should be used after meals, washed down with a glass of water.
Adults and children over 12 years of age: 2 capsules 3 times a day.
The maximum daily dose of 12 capsules (1.2 g of ibuprofen) should not be exceeded.
The total duration of treatment at the recommended dose should not exceed 20 days.
Overdose.
In case of overdose, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, sleep disturbances and tinnitus may occur. In severe cases, arterial hypertension, metabolic acidosis, loss of consciousness, impaired liver and kidney function or hepatonecrosis may occur.
Treatment: symptomatic, aimed at ensuring the vital functions of the body and normalizing the condition. Gastric lavage and oral administration of activated charcoal are recommended within 1 hour after the use of a potentially toxic dose of the drug (more than 400 mg/kg) and hospitalization in the toxicology department. In the inpatient stage, infusion therapy, forced diuresis, symptomatic treatment are used. There are no specific antidotes.
Side effects.
Most of the side effects after using the drug Artiflex Ultra are caused by ibuprofen and are dose-dependent. Since the recommended single dose of ibuprofen is moderate, and the usual daily dose in the drug Artiflex Ultra (600 mg) is significantly lower than its maximum daily dose (1200 mg), it is unlikely that any side effects will be observed if the drug is used according to the dosage recommendations. With long-term treatment of chronic conditions, additional side effects may occur.
From the gastrointestinal tract. Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, diarrhea, flatulence, constipation and vomiting. Heartburn, ulcerative stomatitis, peptic ulcers, melena, perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding may occur, which in some cases can be fatal, especially in the elderly. In isolated cases, exacerbation of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease has been reported.
From the nervous system. Headache, depression of consciousness and disorientation, aseptic meningitis (isolated cases have been reported). Dizziness, irritability, nervousness, tinnitus, depression, drowsiness, insomnia, anxiety, psychomotor agitation, emotional instability, convulsions may occur.
From the urinary system. There are reports of acute renal failure, papillonecrosis, especially with prolonged use, in combination with increased serum urea and edema. Ibuprofen can cause cystitis and hematuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, oliguria, polyuria, glomerulonephritis, tubular necrosis, glomerulonephritis.
From the hepatobiliary system. Liver disorders may occur, especially with prolonged use, in the form of hepatitis, jaundice, pancreatitis, duodenitis, esophagitis, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatonecrosis, liver failure.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders. Hematopoietic system disorders (anemia, neutropenia, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, eosinophilia, decreased hematocrit and hemoglobin levels, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis). The first signs are high fever, sore throat, mouth ulcers, flu symptoms, severe exhaustion, unexplained bleeding and bruising. Reversible platelet aggregation, alveolitis, pulmonary eosinophilia.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders. In rare cases, severe forms of skin reactions such as erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis may occur. Skin peeling, alopecia, photosensitivity may occur.
Immune system disorders: Severe hypersensitivity reactions with the following manifestations: swelling of the face, tongue and larynx, shortness of breath, angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
In patients with autoimmune disorders (systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic connective tissue diseases) during treatment with ibuprofen, isolated cases of symptoms of aseptic meningitis were observed, namely: stiffness of the occipital muscles, headache, nausea, vomiting, high fever or disorientation.
Cardiovascular system and cerebral circulation. Edema, arterial hypertension and heart failure have been reported during treatment with NSAIDs. Long-term use of ibuprofen in high doses (2400 mg/day) may lead to a slight increase in the risk of arterial thromboembolism or stroke. Cerebrovascular disorders may occur. Arterial hypotension, palpitations.
Visual organs. Blurred vision, change in color perception, toxic amblyopia.
Others. Changes in the endocrine system and metabolism, decreased appetite, dry mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth, rhinitis, hearing impairment.
Artiflex Ultra should be discontinued if any adverse reaction occurs and consult a doctor immediately.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other types of interactions. When used simultaneously with the drug Artiflex Ultra capsules, interactions with the following medicinal products may be observed:
Acetylsalicylic acid
Ibuprofen has been shown to inhibit platelet aggregation by acetylsalicylic acid. This effect may be significant when enteric-coated acetylsalicylic acid preparations are used and/or high doses of ibuprofen are used. If immediate-release (non-enteric-coated) acetylsalicylic acid preparations are used, a single dose of ibuprofen may be administered 2 hours after the salicylate or at least 8 hours before acetylsalicylic acid to prevent attenuation of the effects of the latter.
Cyclosporine
Concomitant use may increase the risk of nephrotoxic effects.
Lithium
The level of lithium in the blood plasma increases.
Methotrexate at doses of 15 mg/week or higher:
Increased methotrexate concentrations and increased risk of methotrexate toxicity.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Increased risk of erosive-ulcerative lesions and gastrointestinal bleeding (See Contraindications).
Anticoagulants
NSAIDs may enhance the effects of anticoagulants such as warfarin.
Corticosteroids
Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding or ulceration.
Antihypertensives and diuretics
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may reduce the therapeutic effect of these drugs.
Antiplatelet drugs and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Cardiac glycosides
NSAIDs can exacerbate heart failure and increase the level of glycosides in the blood.
Zidovudine
There is evidence of an increased risk of hemarthrosis and hematoma in HIV-infected patients receiving concomitant treatment with zidovudine and ibuprofen.
Mifepristone
NSAIDs should not be used earlier than 8-12 days after mifepristone administration, as they reduce its effectiveness.
Tacrolimus:
There may be an increased risk of nephrotoxicity with concomitant use of NSAIDs and tacrolimus.
Potassium-sparing diuretics
Hyperkalemia may occur.
Alcohol
Increased risk of gastrointestinal damage and prolonged bleeding.
Quinolone antibiotics
Concomitant use of NSAIDs and quinolone antibiotics may increase the risk of seizures.
Tetracycline
Increases the absorption of tetracycline from the gastrointestinal tract.
Penicillin
Penicillin absorption is reduced.
Chloramphenicol
The absorption of chloramphenicol is reduced.
Shelf life: 2 years.
Storage conditions. Store in original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25? C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Be the first to review “Artiflex Ultra capsules 60 pcs.” Cancel reply
You may also like








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.