No products in the cart.
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more
We deliver to:
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more
Motherwort tablets of 14 mg, 4...
$13.99 Original price was: $13.99.$12.69Current price is: $12.69.


Corvaltab Extra film-coated ta...
$17.49 Original price was: $17.49.$15.89Current price is: $15.89.
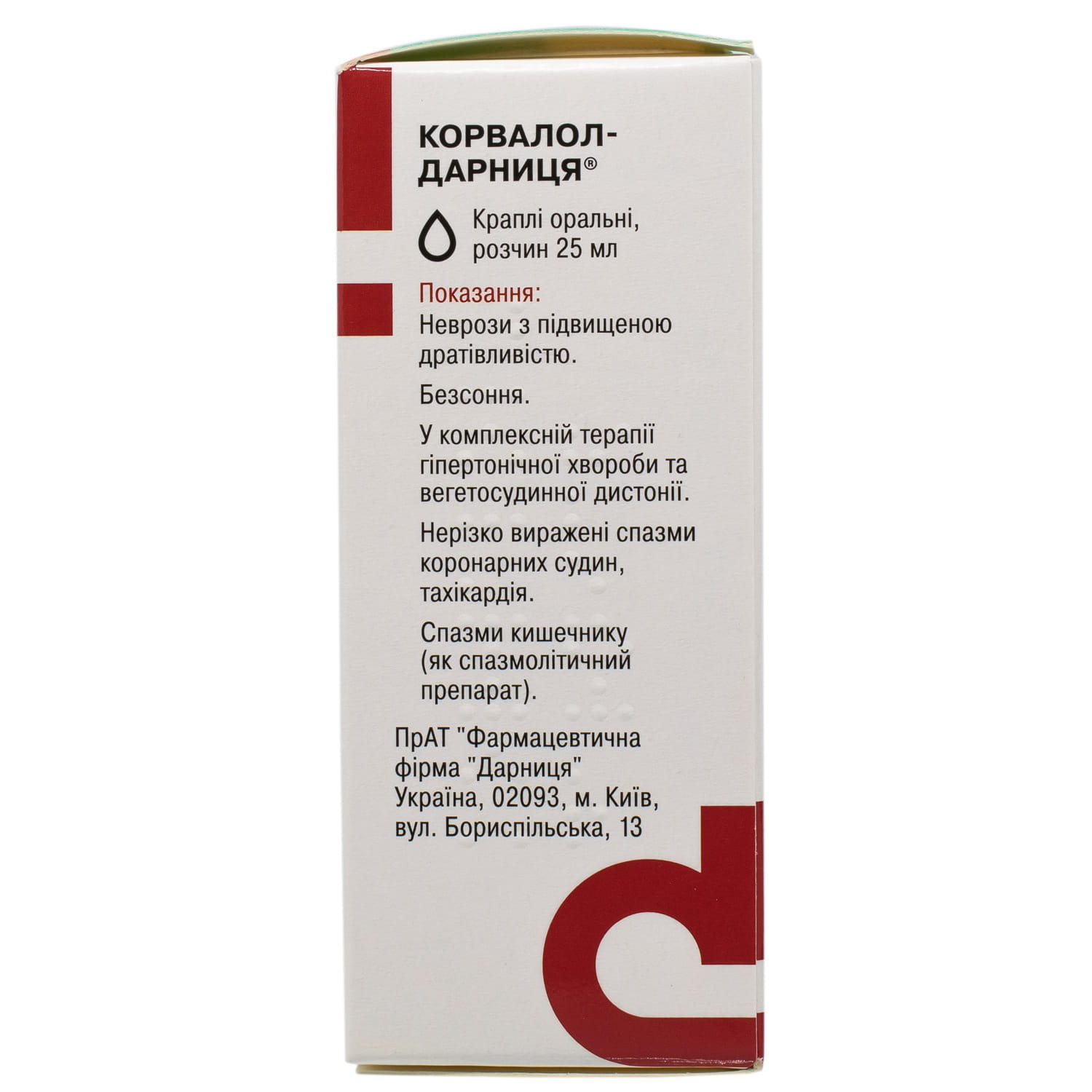
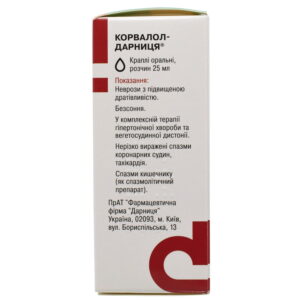
Corvalol Darnytsia drops, oral solution, bottle of 25 ml
$15.09 Original price was: $15.09.$13.69Current price is: $13.69.
Free Worldwide Shipping
to: Australia, Canada, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Poland, South Korea, Switzerland, United Kingdom, United States and more
In stock
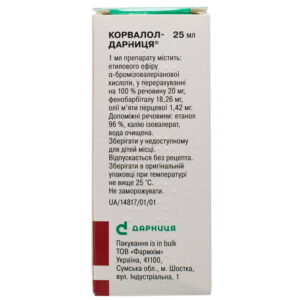
Corvalol Darnytsia Drops are a trusted herbal-based solution designed to provide calming and sedative effects for individuals dealing with stress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances. This oral solution contains a combination of active ingredients including phenobarbital, ethyl bromisovalerianate, and peppermint oil, which work together to help reduce nervous tension, promote relaxation, and ease mild insomnia.
Payment
PayPal, Debit or Credit card, Google Pay, Apple Pay
Pharmacological properties
Corvalol-Darnytsia has a sedative and antispasmodic effect, which is determined by its components.
Thus, the reflex sedative effect occurs due to the ethyl ester of α-bromosovaleric acid. In addition, this substance has antispasmodic properties.
Phenobarbital suppresses the reticular formation, which activates the cerebral cortex. This leads to the development of a sedative effect, a decrease in nervous tension or a hypnotic effect (determined by the dose).
As a result of taking the drug, the activating effect on the vascular center, peripheral vascular system and coronary vessels of the heart is weakened.
The irritating effect of menthol and its esters contained in peppermint oil on the cold receptors of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity contributes to:
- reflex vasodilatation of cerebral vessels and heart vessels;
- relief of spasm of smooth muscles;
- the emergence of a sedative effect.
Peppermint oil also causes:
- antispasmodic effect;
- slight choleretic effect;
- disinfecting properties;
- increased intestinal peristalsis;
- elimination of excessive accumulation of gases in the digestive tract.
Pharmacokinetics. After oral administration, absorption begins already in the regio sublingualis. The components of the drug are characterized by high bioavailability – about 60-80%. When used sublingually or on lump sugar, the development of action occurs the fastest – 5-10 minutes after administration. The effect increases after 15-45 minutes and lasts 3-6 hours. The period of activity decreases in patients who have previously used barbiturates. This is due to the induction by drugs of this group of metabolic enzymes in the liver. Patients with cirrhotic changes in the liver and elderly patients are characterized by a decrease in the hepatic metabolism of the drug. This leads to an increase in T ½ and requires a corresponding correction (decrease) in the dose of the drug, as well as an increase in the time period between its administrations.
Indication
Neuroses (hypersthenic form); insomnia; vegetative-vascular dystonia and ag (as part of complex treatment); spasm of the coronary arteries of the heart (slightly pronounced), increased heart rate (90 beats / min); as an antispasmodic for intestinal spasm.
Application
Per os 15-30 drops with water or on a piece of sugar 2-3 times a day. food intake does not affect the intake of the drug. a single dose can be increased to 40-50 drops in case of a marked increase in heart rate and spasm of the coronary arteries of the heart.
The duration of use is determined by the doctor (determined by the tolerability of the drug and its clinical effectiveness).
Contraindication
Increased sensitivity to the components of the drug, bromine; pronounced liver and / or kidney function disorders; hepatic forms of porphyria; severe heart failure.Medicinal products containing phenobarbital are not used:
- with drug and medication addiction; alcoholism;
- in patients with depression;
- with pathology of the respiratory system, which is accompanied by shortness of breath, obstructive syndrome;
- in patients with diabetes;
- with a decrease in blood pressure (pronounced);
- in case of acute myocardial infarction;
- with myasthenia;
- during pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- if the patient’s age is ≤18 years (there are no data on use in the specified age group).
Side effects
- corvalol-Darnytsia is generally well tolerated.
Side effects, possible in some cases, are as follows:
- digestive system: constipation, a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric area.
Long-term use of the drug can cause liver dysfunction, episodes of nausea or vomiting;
- nervous system: dizziness (slightly pronounced), impaired coordination of movements, ataxia, nystagmus, weakness, fatigue, slowing down of the speed of reactions, hallucinations, headache, disorders of cognitive functions, confusion, drowsiness, paradoxical excitement, decreased concentration of attention;
- immune system: hypersensitivity reactions (including Quincke’s edema);
- skin and mucous membranes: allergic reactions (including skin rash, itching, urticaria), as well as Lyell’s and Stevens-Johnson syndromes (especially possible in the first weeks of treatment);
- blood system: anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis;
- respiratory system: difficult breathing;
- cardiovascular system: decrease in heart rate, arterial hypotension;
- musculoskeletal system: the risk of bone tissue formation disorders (noted with long-term use of phenobarbital as part of medicines).
A long period of reception can lead to the development of symptoms of bromine intoxication.
If the dose is reduced or the drug is discontinued, these effects disappear.
Special instructions
Drowsiness and dizziness, coordination disorders, a decrease in the speed of psychomotor reactions during the use of the drug can be caused by its components – phenobarbital and ethanol. therefore, types of activity that require quick response and concentration of attention are not recommended during the period of use of the drug.
The drug can cause drug dependence during a long period of administration.
The ethanol content in the preparation is 56 vol.%.
Do not combine with alcohol.
It is necessary to show foresight in patients with epilepsy, as well as in patients with liver pathology.
Interactions
The effect of the drug is enhanced when combined with drugs of central action (depressant type). valproate and ethanol also enhance the effect of corvalol-Darnytsia.
Induction of liver enzymes by phenobarbital can lead to a decrease in T ½ in drugs whose biotransformation occurs in the liver.
Taking phenobarbital leads to an increase in the effect of painkillers and drugs for local anesthesia.
An increase in the period of action of phenobarbital occurs against the background of the use of MAO inhibitors.
Simultaneous use with rifampicin reduces the activity of phenobarbital.
The drug enhances the toxic properties of methotrexate. Simultaneous administration with zidovudine leads to increased toxicity of both zidovudine and methotrexate.
Long-term use in combination with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs leads to the risk of stomach ulcers, including those complicated by bleeding. Combined use with gold preparations increases the risk of kidney damage.
Overdose
Accumulation of the components of the drug in the body is possible as a result of its long-term or frequent intake. with an increase in the period of use, psychomotor excitement, addiction and withdrawal syndrome may develop.
Manifested by suppression of CNS functions (including to coma), respiratory suppression (including to cessation of breathing), suppression of cardiovascular activity (including cardiac arrhythmias), lowering of blood pressure (including to a mild form of collapse), lowering of body temperature , decreased education and excretion of urine, nausea and weakness.
Storage conditions
At a temperature ≤25 °C in the original packaging. do not expose to freezing.
Be the first to review “Corvalol Darnytsia drops, oral solution, bottle of 25 ml” Cancel reply
You may also like







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.