🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more
🇦🇺 Australia
🇨🇦 Canada
🇨🇿 Czechia
🇩🇰 Denmark🇪🇪 Estonia
🇮🇪 Ireland
🇮🇱 Israel
🇮🇹 Italy
🇯🇵 Japan
🇲🇽 Mexico
🇵🇱 Poland
🇰🇷 South Korea
🇨🇭 Switzerland
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
🇺🇸 United States of Americaand more
Nurofen for children rectal suppositories (candles) 60 mg 10 pcs.
$16.21
Nurofen for Children suppositories relieve mild to moderate pain and fever when oral intake isn’t possible, providing fast, effective symptom relief.
-
— or —
Nurofen for Children suppositories are used for the following indications: for the symptomatic treatment of mild to moderate pain, for the symptomatic treatment of fever. These suppositories are recommended when oral administration is not possible, for example, in case of vomiting.
Composition
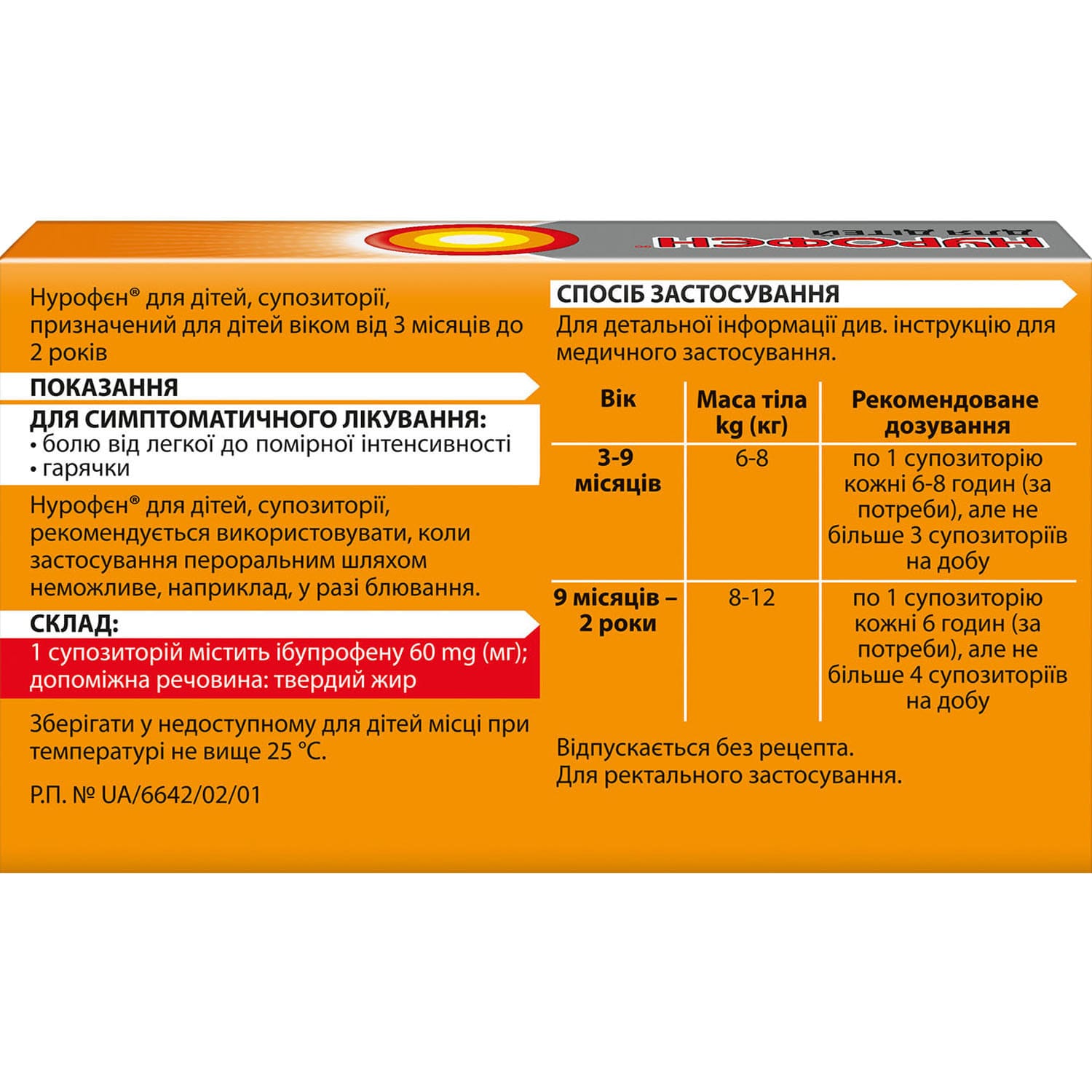
The active substance is ibuprofen (1 suppository contains 60 mg of ibuprofen).
The excipient is solid fat.
Contraindication
- hypersensitivity to ibuprofen or other NSAIDs or to any of the excipients;
- history of hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. bronchospasm, angioedema, bronchial asthma, rhinitis, urticaria) after taking acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), ibuprofen or other NSAIDs;
- gastric ulcer/bleeding in active form or history of recurrence (two or more severe episodes of confirmed ulcer or bleeding);
- history of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation associated with NSAID use;
- severe liver failure, severe kidney failure, or severe heart failure;
- severe dehydration (caused by vomiting, diarrhea, or insufficient fluid intake);
- the last trimester of pregnancy;
- cerebrovascular or other bleeding in the active phase.
- hematopoietic disorders of unknown etiology;
- Do not use in children weighing less than 6 kg and up to 3 months.
Method of application
The drug is intended for rectal use. For short-term use only.
This medicine should only be used in children aged 3 months and over with a body weight of at least 6 kg. The maximum single dose should not exceed 10 mg/kg body weight. The dosing interval should not be less than 6 hours. The maximum daily dose of ibuprofen is 20-30 mg/kg body weight, divided into 3-4 single doses.
Children weighing 6-8 kg (3-9 months): at the beginning of treatment – 1 suppository. If necessary, another suppository can be used, but not earlier than after 6-8 hours. Do not use more than 3 suppositories within 24 hours.
Children weighing 8-12 kg (9 months – 2 years): at the beginning of treatment – 1 suppository. If necessary, another suppository can be used, but not earlier than after 6 hours. Do not use more than 4 suppositories within 24 hours.
This medication is contraindicated in children weighing less than 6 kg and up to 3 months of age.
Patients with kidney or liver failure should consult a doctor before using this medication.
If symptoms worsen or persist in children 3-5 months of age after 24 hours of treatment, you should consult a doctor immediately.
If symptoms persist for more than 3 days after the start of treatment or worsen in children aged 6 months and older, you should consult a doctor.
Side effects can be minimized by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time necessary to control symptoms.
Application features
Pregnant women
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect pregnancy and/or embryonal/fetal development. Epidemiological data indicate an increased risk of miscarriage, congenital heart defects and gastroschisis after use of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors in early pregnancy. Ibuprofen is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy.
Ibuprofen and its metabolites pass into breast milk in low concentrations. To date, there is no data on negative effects on the infant, so for short-term treatment of pain and fever at recommended doses, it is usually not necessary to interrupt breastfeeding.
There is some evidence that drugs that inhibit cyclooxygenase/prostaglandin synthesis may impair female fertility by affecting ovulation. This effect is reversible upon discontinuation of treatment.
Drivers
When used according to the recommended doses and duration of treatment, the drug is not expected to affect the ability to drive or use other mechanisms.
Overdose
The use of a dose of 200 mg/kg body weight in children may cause intoxication.
Symptoms
Symptoms of overdose may include nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain or, less commonly, diarrhea. Nystagmus, blurred vision, tinnitus, headache and gastrointestinal bleeding may also occur. In more severe poisoning, toxic effects on the central nervous system may occur in the form of vertigo, dizziness, drowsiness, sometimes – an excited state and disorientation or coma. Sometimes patients develop convulsions. In severe poisoning, hyperkalemia and metabolic acidosis may occur, as well as an increase in PV / INR (probably due to interaction with blood clotting factors circulating in the bloodstream). Acute renal failure, liver damage, hypotension, respiratory depression and cyanosis may occur. In patients with bronchial asthma, exacerbation of the course of asthma is possible.
Treatment
There is no specific antidote. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive, including maintaining a patent airway and monitoring cardiac function and vital signs until the patient is stable.
Side effects
The most frequently observed adverse reactions are from the gastrointestinal tract. In general, adverse reactions are dose-dependent. In particular, the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding depends on the dose and duration of treatment. Gastrointestinal ulcers, perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding, sometimes fatal, may occur, especially in elderly patients. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal distension, constipation, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, melena, haematemesis, ulcerative stomatitis, exacerbation of colitis and Crohn’s disease have been reported after the use of ibuprofen. Gastritis has been observed less frequently.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C, out of the reach of children.
You may also like








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.