The drug should be prescribed with caution and in doses below the average therapeutic dose, in severe heart diseases, supraventricular tachycardia, respiratory depression, decreased intestinal peristalsis, shock conditions, weakened patients and the elderly.
It is not recommended to use the drug for long-term treatment of hypertension, especially in elderly patients.
When taking the drug, the development of orthostatic hypotension is possible.
If symptoms of liver dysfunction appear, in particular, gastrointestinal disorders, jaundice, eosinophilia and increased liver enzymes, it is necessary to stop taking the drug.
You should inform your doctor about the following symptoms: hot flashes, increased sweating, headache, increased fatigue, jaundice, skin rash, nausea, stomach discomfort, constipation.
Smoking reduces the effectiveness of the medicine.
While taking the drug, you should avoid drinking alcohol and drugs that depress the CNS.
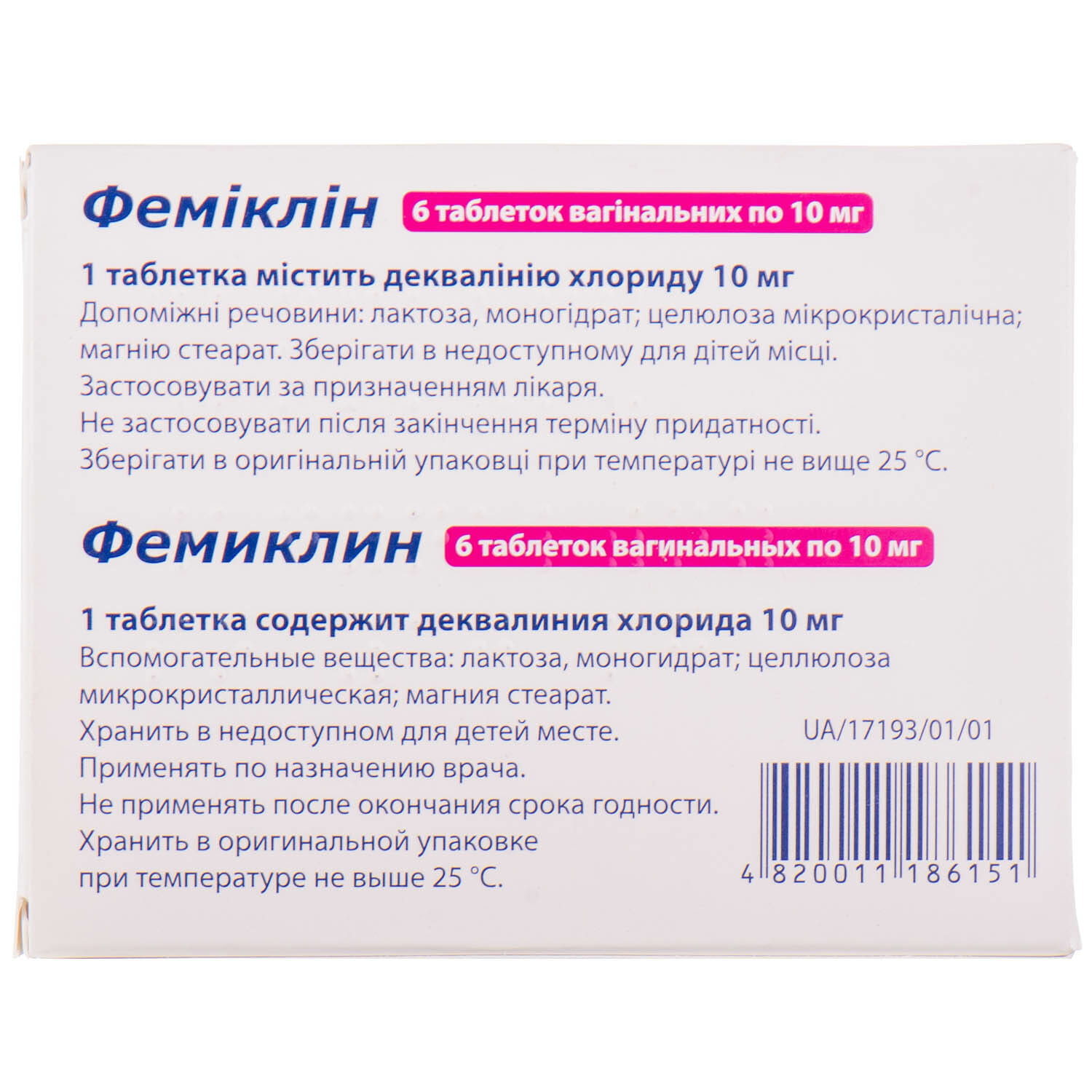
The medicine contains lactose, therefore patients with rare hereditary forms of galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome should not take the medicine.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Children. The drug should not be used in children.
Ability to influence the speed of reactions when driving vehicles or other mechanisms. During treatment with the drug, you should refrain from driving vehicles or working with other complex mechanisms.

































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.