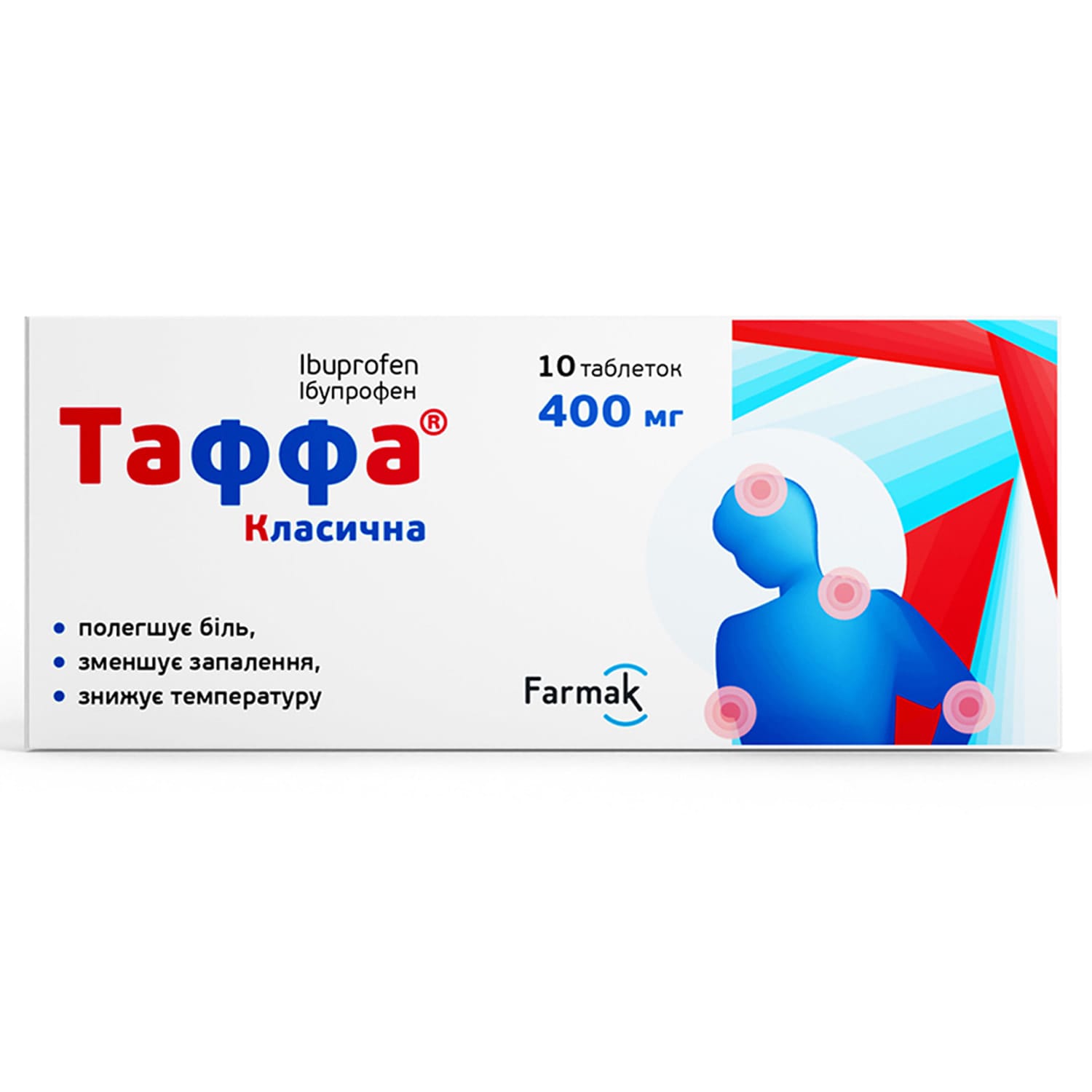
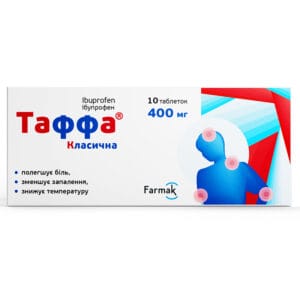
Taffa Classic – nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic agent. Propionic acid derivatives.
Indications for use
Symptomatic treatment of headaches, including migraines, toothaches, dysmenorrheal pain, neuralgia, back pain, muscle pain, rheumatic pain (except for severe cases of arthritis), as well as cold and flu symptoms, fever.
Composition
- active ingredient: ibuprofen;
- 1 film-coated tablet contains ibuprofen – 400 mg;
- excipients: microcrystalline cellulose; croscarmellose sodium; lactose monohydrate; colloidal anhydrous silica; sodium lauryl sulfate; magnesium stearate;
- film coating: hypromellose; titanium dioxide (E 171); macrogol.
Contraindication
- Hypersensitivity to ibuprofen or to any of the components of the drug.
- History of hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. bronchial asthma, rhinitis, angioedema or urticaria) following previous use of ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid/aspirin or other NSAIDs.
- Third trimester of pregnancy.
- Gastric and/or duodenal ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding in active form, or history of recurrence (two or more severe episodes of confirmed ulcer or bleeding in the past).
- Acute or previous inflammatory bowel diseases (such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis).
- History of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation associated with NSAID use.
- Increased tendency to bleed.
- Severe liver failure (cirrhosis, ascites).
- Severe renal failure (creatinine clearance <30 ml/min).
- Severe heart failure (New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III-IV).
- Treatment of postoperative pain after coronary artery bypass graft surgery (or use of a heart-lung machine).
Adverse reactions
The most common adverse reactions observed with NSAIDs are those affecting the gastrointestinal tract. Peptic ulcers, perforations or bleeding, sometimes fatal, especially in elderly patients, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence, constipation, indigestion (dyspepsia), abdominal pain, melena, hematemesis may occur.
Ulcerative stomatitis, exacerbation of colitis and Crohn’s disease have been reported following use. Gastritis is less common. Gastrointestinal perforation has been reported rarely with ibuprofen.
Exacerbation of skin infections caused by infection (e.g. development of necrotizing fasciitis) has been described with concomitant use of NSAIDs. If there are any signs of infection or it worsens while using ibuprofen, the patient should consult a doctor immediately.
Method of application
For short-term use only. Use the lowest effective dose necessary to relieve symptoms for the shortest period of time.
Most patients can take Taffa Classic on an empty stomach without stomach upset.
Adults and children over 12 years of age. Take 1 tablet every 6 hours. Swallow the tablets with water. Do not take more than 3 tablets in 24 hours. The maximum daily dose is 1200 mg.
Application features
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding
During the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, ibuprofen should not be prescribed unless clearly necessary. If ibuprofen is used by a woman attempting to conceive, or during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy, the dose should be kept as low and the duration of treatment as short as possible.
The drug Taffa® Classic is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy.
NSAIDs pass into breast milk. For safety reasons, ibuprofen is not recommended for use in breastfeeding women. If treatment is necessary, the infant should be transferred to formula feeding.
Children
The drug Taffa® Classic should not be used in children under 12 years of age.
The ability to influence the reaction speed when driving or working with other mechanisms
No relevant studies have been conducted. However, it is known that ibuprofen can sometimes have side effects on the central nervous system, such as a reduction in reaction time. This should be taken into account when increased alertness is required, especially when driving or operating machinery. This is especially the case when taken with alcohol.
Overdose
Symptoms of toxicity have not usually been observed in children or adults at doses below 100 mg/kg body weight. However, supportive measures may be necessary in some cases. In children, symptoms of toxicity have been observed after doses of 400 mg/kg or more.
Symptoms. In most patients who have taken a significant amount of ibuprofen, symptoms develop within 4-6 hours. The most commonly reported symptoms of overdose are nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, drowsiness and lethargy. Central nervous system (CNS) side effects include headache, tinnitus, dizziness, convulsions and loss of consciousness. Nystagmus, metabolic acidosis, hypothermia, renal damage, gastrointestinal bleeding, coma, apnea and CNS and respiratory depression have been reported rarely. Cardiovascular toxicity, including hypotension, bradycardia and tachycardia, has also been reported. In the event of a significant overdose, renal failure and liver damage may develop. A significant overdose is usually well tolerated if no other drugs are taken.
Treatment. There is no specific antidote for ibuprofen overdose. Patients should be treated symptomatically if necessary. After ingestion of a potentially toxic amount, activated charcoal should be administered within one hour. If necessary, serum electrolyte balance should be corrected.
If the medication has already been absorbed, alkalizing agents should be given to help eliminate ibuprofen in the urine.
Storage conditions
Does not require special storage conditions.
Keep out of reach of children.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.